- So, I think that DAX is a pain in the butt to use and to learn. I talk about that in my intro to DAX presentation, but I think it boils down to the fact that you need a bunch of mental concepts to have a proper mental model, to simulate what DAX will do. This is very deceptive, because it looks like Excel formulas on steroids, but conceptually it’s very different.
Here is the problem with DAX, in a nutshell:
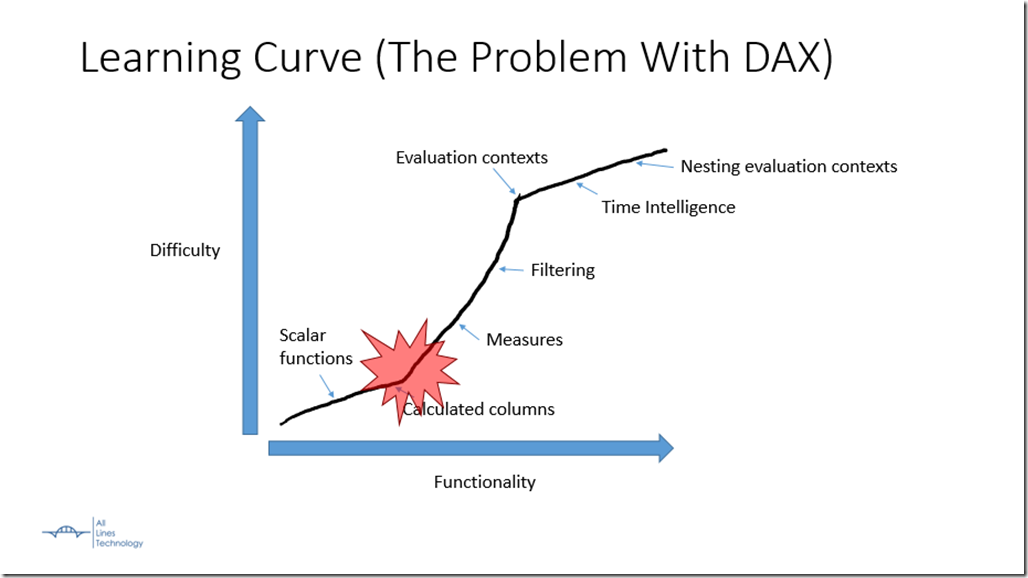
This example below is a perfect example of that sharp rise in learning curve, and dealing with foreign concepts like calculated columns, measures, applied filters, and evaluation contexts.
So, one of the things I’m hoping to catalog are example where DAX is a giant pain if you don’t know what you are doing. People make it look really simple and smooth, and that can be frustrating sometimes. Let’s see more failures!
How do I GROUPBY in DAX?
John Hohengarten asked me a question recently on the SQL Community Slack. He said:
I need to sum an amount column, grouped by a column
Measure 1 :=
GROUPBY (
det,
det[nbr],
“Total AR Amt Paid calc”, SUM ( det[amt] )
)
I’m getting a syntax error
So automatically, something seemed off to me. Measures are designed to return a single value, given the filter context that’s applied to them. That means you almost always need some aggregate function at an outer level. But based on the name, you wouldn’t necessarily expect GROUPBY to return a single value. It would return values for each grouping instance.
If we take a look at the definition for GROUPBY(), we see it returns a table, which makes sense. But if you are new to DAX, this is really unintuitive because DAX works primarily in columns and tables. This is a really hard mental shift, coming from SQL or Excel.
What do you really want?
None of this made any sense to me. Why would you try to put a GROUPBY in a measure? That’s like trying to return an entire table for a KPI on a dashboard. It just doesn’t make sense. So I asked John what he was trying to do.
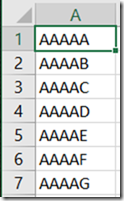
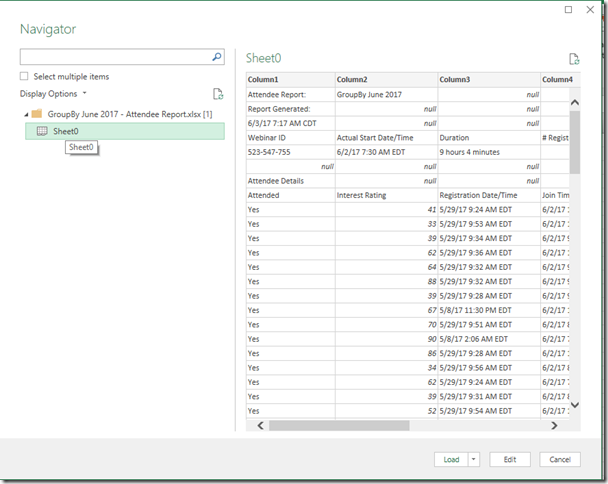
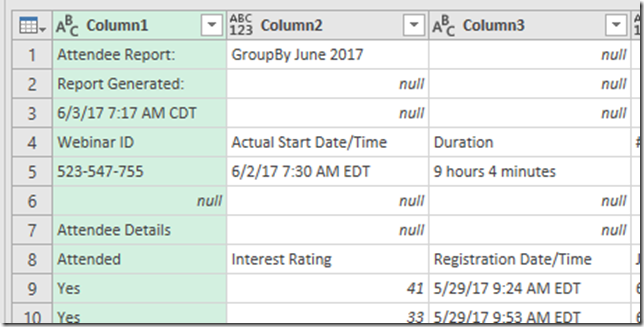
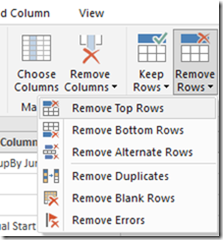
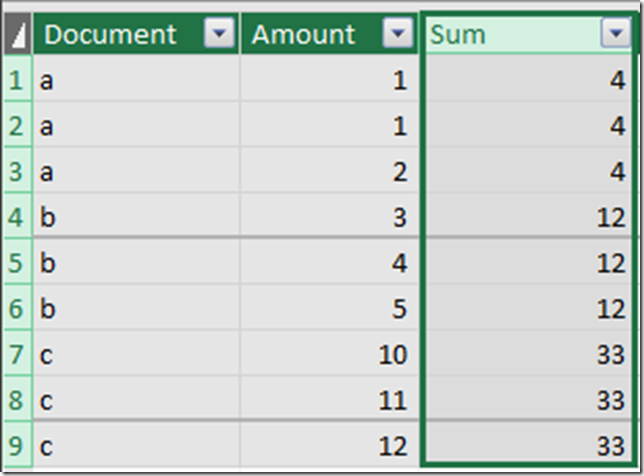
He sent me an image of some data he was working with. On the far left is the document id and on the far right is the transaction amount.
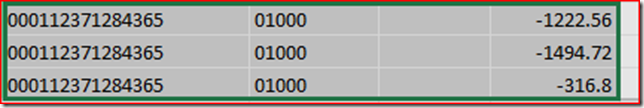
He wanted to add another column on the right, that summed up all of the amounts for transactions with the same document. In SQL, you’d probably do this using a Window function with a SUM aggregate, like here.
Calculated columns versus measures
This highlights another piece of DAX that is unintuitive. You have two ways of adding business logic: calculated columns and measures. The both use DAX, both look similar and are added in slightly different spots.
But semantically and technically, they are very different beasts. Calculated columns are ways of extending the table with new columns. They are very similar to persisted, computed columns in SQL. And they don’t care at all about your filters or front-end, because the data is defined at time of creation or time of refresh. Everything in a calculated column is determined long before you are interacting with them.
Measures on the other hand, are very different. They are kind of like custom aggregate functions, like if you could define your own version of SUM. But to carry the analogy, it would be like if you had a version of SUM that could manipulate the filters you applied in your WHERE clause. It gets weird.
My point is, if you don’t grok the difference between calculated columns and measures, you will never be able to work your way around the problem. You will be forced to grope and stumble, like someone crawling in the dark.
Filter context versus row context
So in this case we’ve determined we actually want to extend the table with a column, not create a free-floating measure. Now we run headlong into our next conceptual problem: evaluation contexts.
In DAX there are two types of evaluation contexts: row contexts and filter contexts. I won’t go too deep here, but they define what a formulas can “see” at any given time, and in DAX there are many ways to manipulate these contexts. This is how a lot of the time intelligence stuff works in DAX.
In this case, because we are dealing with a calculated column, we have only a row context, not filter context. Essentially, the formula can only see stuff in the same row. Additionally, if we use an aggregate like SUM, it only cares about the filter context. But the filter context comes from user interaction. Because this data is defined way before that, there is no filter context.
This is another area, where if you don’t understand these concepts you are SOL. Again, for the newbie, DAX is a pain.
What’s the solution?
So what is the ultimate solution to his problem? There are probably better ways to do it, but here is a simple solution I figured out.
SUM =
CALCULATE (
SUM ( Source_data[Amount] ),
ALL ( Source_data ),
Source_data[Document] = EARLIER ( Source_data[Document] )
)
Walking through it, The CALULATE is used to turn our row context, into a filter context. Then it manipulates that filter context so SUM “sees” only a certain set of rows.
The first manipulation is to run ALL against the table, to undo any filters applied to it. In this case, the only filter is our converted row context. (confused yet?)
The next manipulation is to use EARLIER (which is horribly named) to get the value from the earlier row context. In this case we are filtering ALL the rows, to all of them that have the same document. Then, finally we apply the SUM, which “sees” the newly filtered rows.
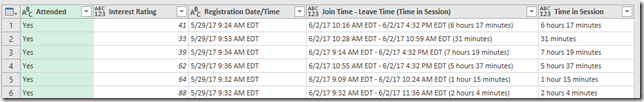
Here is what we get as a result:
How do we verify that?
A fourth pain with DAX is that it’s very hard to look at intermediate stages of a process, like you can with SQL or Excel formulas, but in this case we have a way. If we convert our SUM to a CONCATENATEX, we can output all the inputs as a comma separated list. This gives us a slightly better idea of what’s going on.
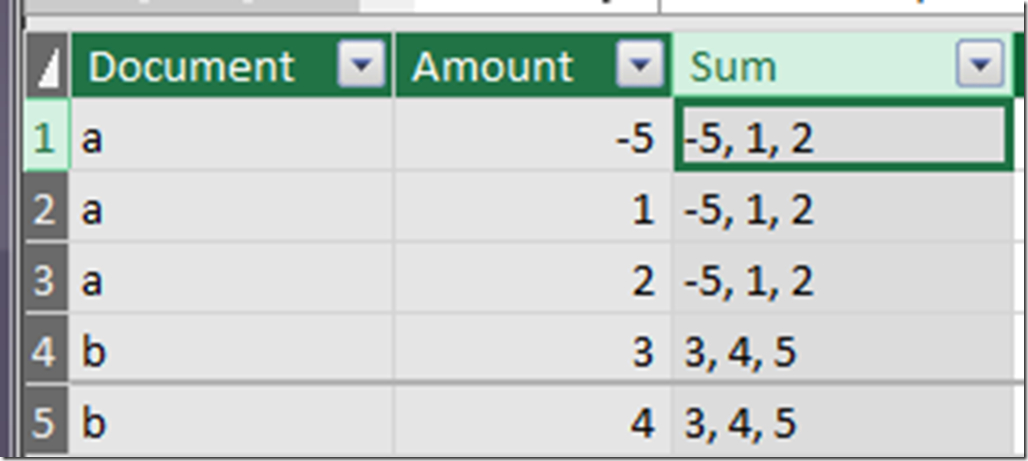
What’s the point?
My point is, that DAX, despite it’s conciseness and richness is hard to start using. Even basic tasks can require complex concepts, and that was a big frustration point for me. You can’t just google GROUPBY and understand what’s going on.
Again, check out my presentation I did for the PASS BI virtual group. I tried to cover all the annoying parts that people new to DAX will run into. That and buy a book! you’ll need it.